Digital LC Meter Version 2
An "improved" inductance / capacitance meter by Phil Rice VK3BHR
Actually, it works much the same as the original.
This version was modified to become a club project for the Midland Amateur Radio Club - http://www.marc.org.au
It differs from the original in that:
- A 16F628 PIC is used. This has internal comparator, which means the LM311 is no longer needed.
- Software calibration is used. The finished meter can be calibrated against "any" accurate capacitor within the range 100pF to about 10000pF.
- A PC Board layout is available (see below).
The Circuit
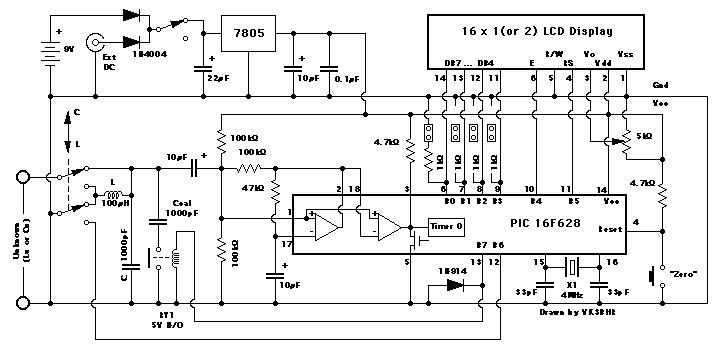
Special Components.
No particularly accurate components are required, except for one (or more) accurately known "external" capacitors used to calibrate the meter.
- The two 1000pF capacitors should be fairly good quality. Polystyrene are preferred. MKT are fine. Greencaps tend to drift in value too much. Avoid ceramic capacitors. Some of these can have high losses (and it is hard to tell).
- The two 10uF capacitors in the oscillator should be tantalum (for low series resistance/inductance).
- The 4MHz crystal should be a genuine 4.000MHz one, not something approximate to 4MHz. Every 1% error in crystal frequency adds 2% error to the indicated inductance value.
- The relay should be a low current one. The PIC can only provide about 30mA of drive current.
- Don't forget the "catch" diode across the relay coil!
PC Board
Board artwork, "ready for ironing on"
Board component layout & and better copy of Circuit diagram
Alternative Board artwork by Peter ZL2VK
The Code
Source code, excluding floating point +-/*
Assembled Hex code (complete, ready to work!)
Alternative Assembled Hex code (also complete, ready to work!)
For displays that show only 8 characters using the other hex file.
Calibration Instructions.
Visit http://www.marc.org.au
Click on the link to LC Meter on the left side of the page (Under the Projects heading).
Here's a copy of it all anyway.
- Check that you have put all the components in the right places.
- Check that you have soldered every lead.
- Double check the PIC orientation, the diode and the 7805.
- Don't forget - the PIC (as purchased) isn't programmed. You gotta load the LC Meter code into it before it will work.
- Apply power carefully. If possible, use a variable regulated supply for the first try. Measure the supply current while gradually increasing the voltage. The current should be below 20mA. The prototype drew just 8mA. If you see nothing on the display and everything else checks out OK, try adjusting the Contrast trimpot. If it is set too far off, you will see nothing. The display should briefly show the word Calibrating, then C=0.0pF (or some other capacitance up to +/- 10pF ).
- Allow several minutes "warm-up", then press the "zero" button to force a re-calibration. The display should now show C=0.0pF.
- Connect your "standard" capacitor. The LC meter should read somewhere near its value (with up to +/- 10% error).
- To raise the indicated capacitance, join the links marked "4" on the diagram below. To lower the indicated capacitance, join the links marked "3" on the diagram below. When the indicated value is "close enough" to the standard, remove the link. The PIC will remember the calibration. You can repeat this as many times as you like (up to 10,000,000 times I think before you wear out the PIC).
- If the meter misbehaves, you can use the links "1" & "2" to check the oscillator frequency. Apply link "2" to check the free running frequency "F1" of the oscillator. This should be shown as 00050000 +/- 10%. If this reading is too high (near 00065535), the meter may go into "numerical overflow" and give you an error message. If the reading is too low (say below 00040000), you will lose some accuracy. Apply link "1" to check the "calibration" frequency "F2". This should be near 71% +/- 5% of the "F1" reading that you get by applying link "2".
- Experts may like to adjust the inductor value to raise F1 to near 00060000 to obtain maximum resolution from the meter. An "L" value of 82uH is preferred instead of the specified 100uH (but you can't buy 82uH inductors in Bendigo).
- If the meter shows near 00000000 for F1 and or F2, then recheck the wiring around the L/C switch, 'cos it sounds like your oscillator has stopped.
- The Inductance measuring function is automatically calibrated when you calibrate the capacitance function. All the testing required is to check that the meter can be "zeroed" with the terminals shorted together.
| Test Links |
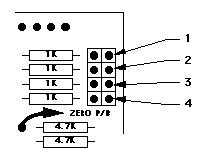 |
- Check F2
- Check F1
- Lower C
- Raise C
|
HELP! It doesn't work.
There is now a "faq". Click this link.
I will add answers as problems arise (as they are bound to do ;-).
Front Panel Artwork by Peter ZL2VK
Click here!

